Klustron(原KunlunBase) 应用连接指南
Klustron(原KunlunBase) 应用连接指南
注意:
如无特别说明,文中的版本号可以使用任何已发布版本的版本号代替。
所有已发布版本详见:Release Notes。
本文目标:
Klustron 支持 PostgreSQL (之后以 PG 简称)和 MySQL 两种连接协议,本文通过命令行和 Python 应用程序两种方式连接 Klustron,并执行多种数据库相关的操作。
连接的计算节点 IP 地址为: 192.168.66.105。
01 检查 PG 和 MySQL 协议分别侦听的端口。
在计算节点执行下面的语句
ps -fu kunlun

从上图看 PG 的侦听端口是 47001, 然后通过 PG 协议登录计算节点数据库,查看 MySQL 的侦听端口。在计算节点上用 kunlun 用户执行下面的命令。
psql -h 192.168.66.105 -p 47001 postgres
show mysql_port;
mysql_port
------------
47002
(1 row)
从上图来看 MySQL 的侦听端口是 47002。
设置环境变量。在计算节点执行下面的命令:
su – klbase
vi Klustron/env.sh
修改红色标注行:
export Klustron=/home/klbase/kunlunbas
eexport KUNLUNVERSION=1.1.1
envtype="${envtype:-no}"
修改后为:
envtype="all"
保存文件后执行下面的命令,使环境变量生效。
. Klustron/env.sh
在计算节点上执行下面的 SQL 创建测试数据库,用户和模式,用于本文之后的测试。
psql -h 192.168.66.105 -p 47001 postgres
create user kunlun_test with password 'kunlun';
create database test_db with owner kunlun_test encoding utf8 template template0;
\q
psql -h 192.168.66.105 -p 47001 -U kunlun_test test_db
create schema testing;
alter user kunlun_test set search_path to testing;
\q
02 使用 PG 客户端连接 Klustron
在任何一个安装 PG 客户端(测试机器安装了 PG 11.18 的客户端)的机器,使用命令行方式以 PG 协议连接计算节点集群数据库,执行创建表和增删改查操作。
psql 客户端连接 Klustron 默认打开了 autocommit。
psql -h 192.168.66.105 -p 47001 -U kunlun_test-d test_db
\echo :AUTOCOMMIT
drop table if exists customer;
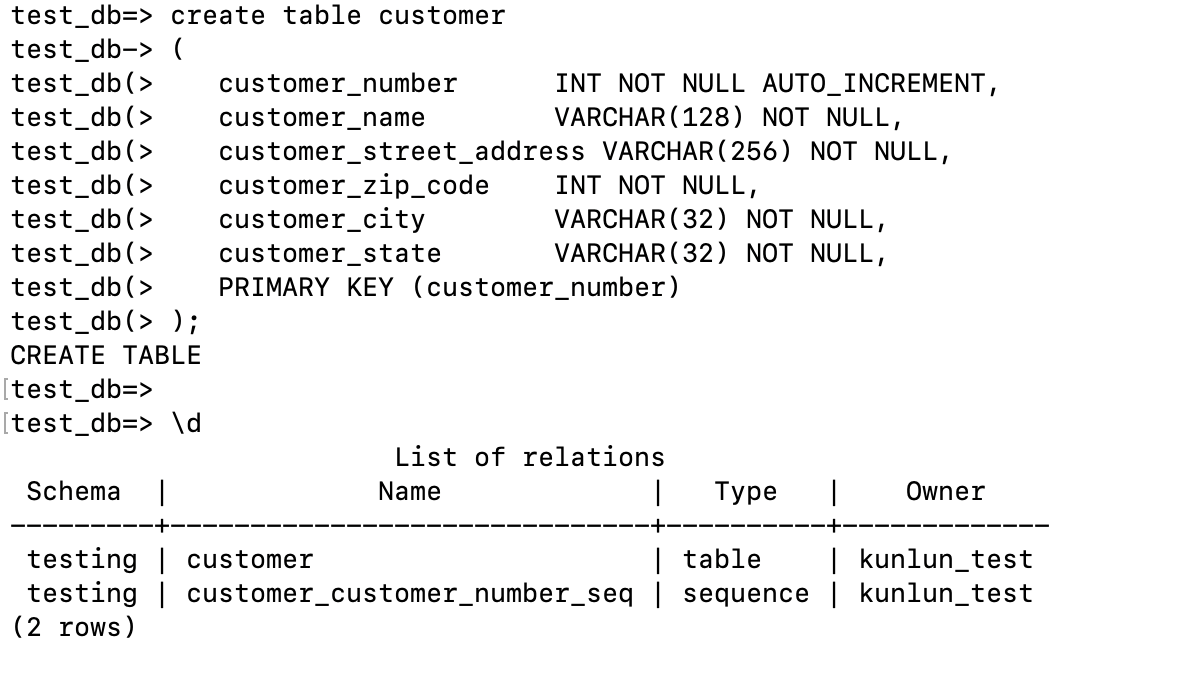
create table customer
(
customer_number INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
customer_name VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
customer_street_address VARCHAR(256) NOT NULL,
customer_zip_code INT NOT NULL,
customer_city VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
customer_state VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (customer_number)
);
\d (MySQL使用show tables;)
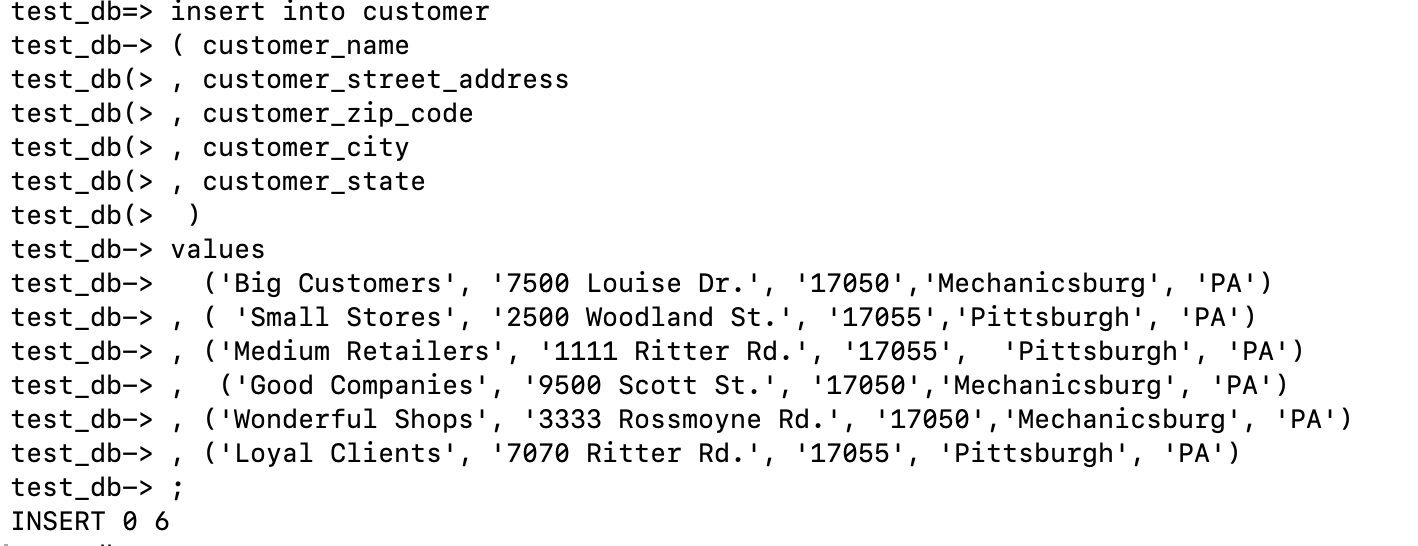
insert into customer
( customer_name
, customer_street_address
, customer_zip_code
, customer_city
, customer_state
)
values
('Big Customers', '7500 Louise Dr.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ( 'Small Stores', '2500 Woodland St.', '17055','Pittsburgh', 'PA')
, ('Medium Retailers', '1111 Ritter Rd.', '17055', 'Pittsburgh', 'PA')
, ('Good Companies', '9500 Scott St.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ('Wonderful Shops', '3333 Rossmoyne Rd.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ('Loyal Clients', '7070 Ritter Rd.', '17055', 'Pittsburgh', 'PA');
select * from customer wherecustomer_number=6;

update customer set customer_state='CA' where customer_number=6 returning customer_number,customer_name,customer_state;

delete from customer where customer_number=6
returning customer_name,customer_street_address;

select * from customer;

03 使用 MySQL 客户端连接 Klustron
在任何安装 MySQL 的机器上使用命令行方式以 MySQL 协议连接计算节点集群数据库,执行创建表和增删改查操作。
MySQL 客户端连接 Klustron 也是默认打开了 autocommit。
mysql -h 192.168.66.105 -P 47002 -u kunlun_test -D test_db -p
show variables like 'autocommit';

其他的创建表,增删改查语句参考上一节相关内容。
04 使用 Python 通过 PG 协议连接
如果系统没有 python3,则需要安装 python3。
yum install python3
验证 python3 是否成功安装。
python3 -Vpip3 -V
设置 python 和 pip 的软链接,配置之后可以直接使用 python、pip 启动
ln -s /etc/alternatives/python3 /usr/bin/python
ln -s /etc/alternatives/pip3 /usr/bin/pip
使用 root 安装 postgresql-devel, 之后安装的 psycopg2 需要依赖于 postgresql-devel。
yum -y install postgresql-devel
pip install psycopg2
编写 kltestpg.py, 具体内容如下:
import psycopg2.extras
conn = psycopg2.connect(database='test_db',user='kunlun_test',
password='kunlun',host='192.168.66.105',port='47001')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor_factory=psycopg2.extras.RealDictCursor)
#drop customer table
drop_sql = "drop table if exists customer;"
cursor.execute(drop_sql)
#create customer table
create_sql = '''CREATE TABLE customer
(
customer_number INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
customer_name VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
customer_street_address VARCHAR(256) NOT NULL,
customer_zip_code INT NOT NULL,
customer_city VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
customer_state VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (customer_number)
); '''
cursor.execute(create_sql)
print("table created")
# insert customer table
insert_sql = '''INSERT INTO customer
( customer_name
, customer_street_address
, customer_zip_code
, customer_city
, customer_state
)
VALUES
('Big Customers', '7500 Louise Dr.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ( 'Small Stores', '2500 Woodland St.', '17055','Pittsburgh', 'PA')
, ('Medium Retailers', '1111 Ritter Rd.', '17055', 'Pittsburgh', 'PA')
, ('Good Companies', '9500 Scott St.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ('Wonderful Shops', '3333 Rossmoyne Rd.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ('Loyal Clients', '7070 Ritter Rd.', '17055', 'Pittsburgh', 'PA')
;'''
cursor.execute(insert_sql)
conn.commit()
print("table inserted")
# query customer table
select_sql = "select customer_name,customer_state from customer"
cursor.execute(select_sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for row in result:
print("Customer Name is:", row['customer_name'],",State is:",row['customer_state'])
# update one row
update_sql = "update customer set customer_state='CA' where customer_name='Big Customers';"
cursor.execute(update_sql)
conn.commit()
print("table updated")
#delete one row
delete_sql = "delete from customer where customer_name='Small Stores';"
cursor.execute(delete_sql)
conn.commit()
print("table deleted")
print("########After table updates and deletes###########")
# select all rows again
select_sql = "select customer_name,customer_state from customer"
cursor.execute(select_sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for row in result:
print("Customer Name is:", row['customer_name'],",State is:",row['customer_state'])
# close cursor
cursor.close()
# close connection
conn.close()
执行输出如下图:
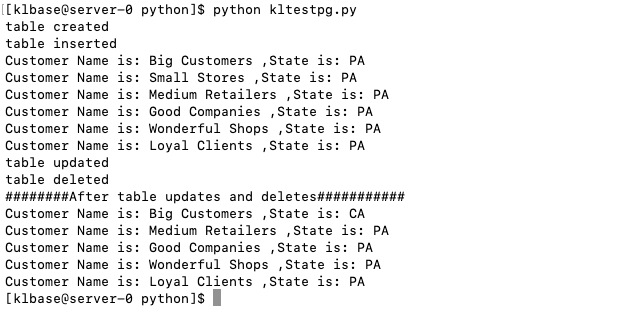
程序逻辑具体如下:
- 创建数据库 test_db 的连接;
- 创建表 customer;
- 在表 customer 中插入 6 行数据;
- 获取表所有行,打印输出;
- 将表中 ’Big Customers’ 对应行的 customer_state 字段从 ’PA’ 修改为 ’CA’;
- 删除表中 ’Loyal Clients’ 对应的行;
- 重新执行全表查询打印输出,可以查看到和 4 的差异。
05 使用 python 通过 MySQL 协议连接
使用 root 安装 pymysql 包。
pip install pymysql
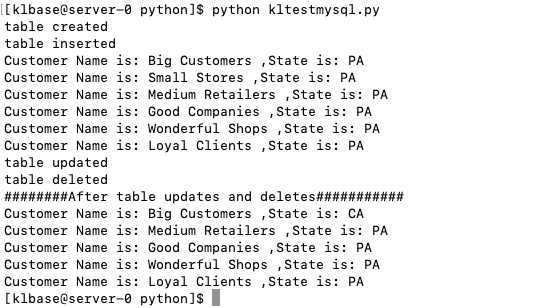
编写 kltestmysql.py, 具体内容如下:
import pymysql
# create connection
conn = pymysql.connect(host='192.168.66.105',
user='kunlun_test',
password='kunlun',
db='test_db',
port=47002,
charset='utf8',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor = conn.cursor()
#drop customer table
drop_sql = "drop table if exists customer;"
cursor.execute(drop_sql)
#create customer table
create_sql = '''CREATE TABLE customer
(
customer_number INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
customer_name VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
customer_street_address VARCHAR(256) NOT NULL,
customer_zip_code INT NOT NULL,
customer_city VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
customer_state VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (customer_number)
); '''
cursor.execute(create_sql)
print("table created")
# insert customer table
insert_sql = '''INSERT INTO customer
( customer_name
, customer_street_address
, customer_zip_code
, customer_city
, customer_state
)
VALUES
('Big Customers', '7500 Louise Dr.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ( 'Small Stores', '2500 Woodland St.', '17055','Pittsburgh', 'PA')
, ('Medium Retailers', '1111 Ritter Rd.', '17055', 'Pittsburgh', 'PA')
, ('Good Companies', '9500 Scott St.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ('Wonderful Shops', '3333 Rossmoyne Rd.', '17050','Mechanicsburg', 'PA')
, ('Loyal Clients', '7070 Ritter Rd.', '17055', 'Pittsburgh', 'PA')
;'''
cursor.execute(insert_sql)
conn.commit()
print("table inserted")
# query customer table
select_sql = "select customer_name,customer_state from customer"
cursor.execute(select_sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for row in result:
print("Customer Name is:", row['customer_name'],",State is:",row['customer_state'])
# update one row
update_sql = "update customer set customer_state='CA' where customer_name='Big Customers';"
cursor.execute(update_sql)
conn.commit()
print("table updated")
#delete one row
delete_sql = "delete from customer where customer_name='Small Stores';"
cursor.execute(delete_sql)
conn.commit()
print("table deleted")
print("########After table updates and deletes###########")
# select all rows again
select_sql = "select customer_name,customer_state from customer"
cursor.execute(select_sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
for row in result:
print("Customer Name is:", row['customer_name'],",State is:",row['customer_state'])
# close cursor
cursor.close()
# close connection
conn.close()
执行输出结果和上一节相同